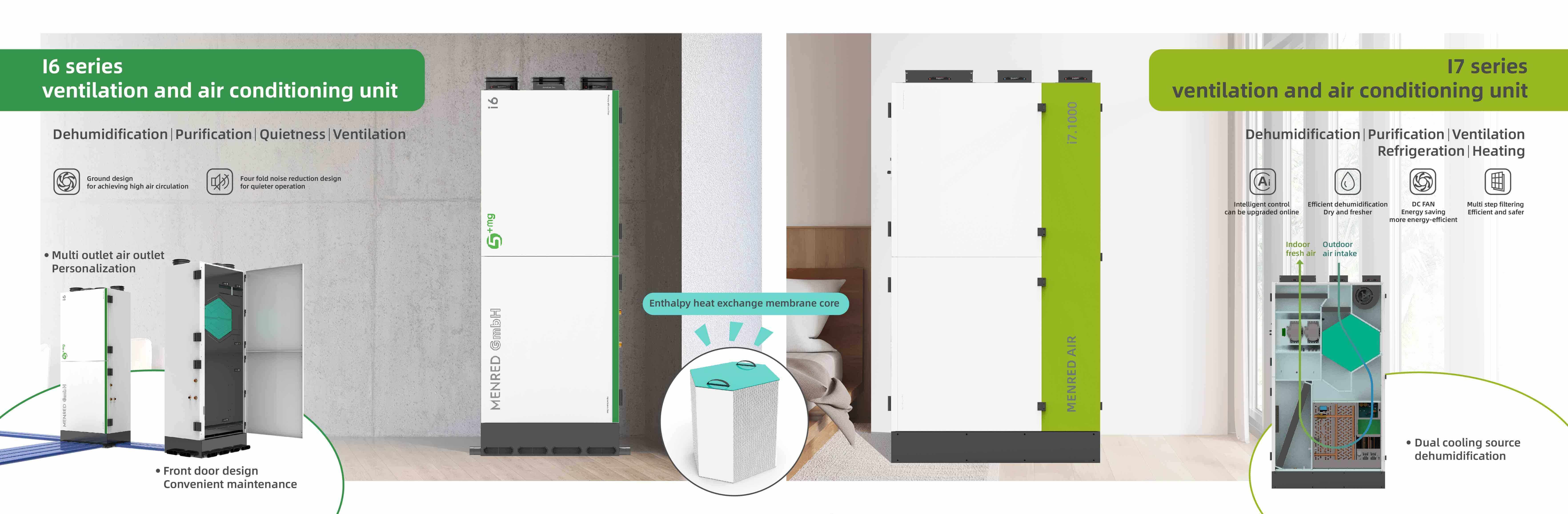
The Ultimate Guide to Enthalpy Heat Exchangers: Efficiency, Functionality, and Benefits
views: 3799 time: 2025-03-17
views: 3799 time: 2025-03-17
In an era where energy efficiency and indoor air quality are top priorities for homeowners and businesses alike, the enthalpy heat exchanger stands out as an essential technology. Whether in residential, commercial, or industrial settings, this advanced ventilation system significantly reduces energy costs while improving air circulation.
But what exactly is an enthalpy heat exchanger, and how does it work? In this comprehensive guide, we will explore its working principle, the difference between enthalpy and heat exchange, and the benefits it brings to modern buildings.
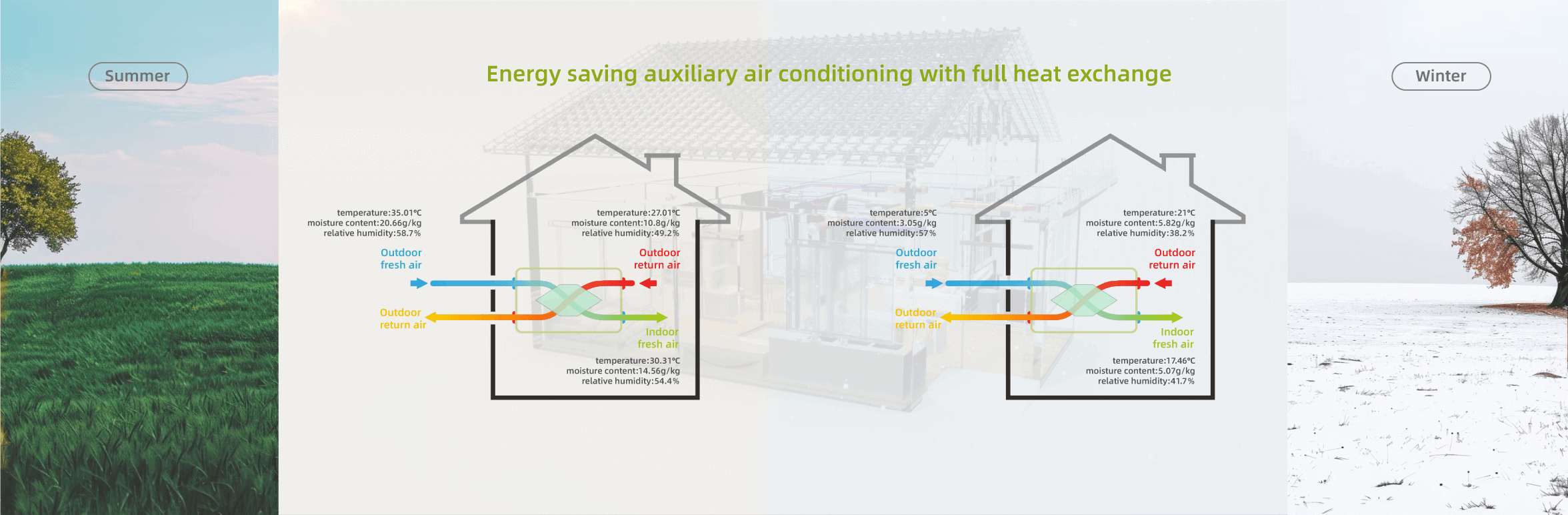
An enthalpy heat exchanger, or energy recovery ventilator (ERV), is a device that recovers energy from exhaust air to precondition incoming fresh air. Unlike traditional systems, Menred's enthalpy exchangers transfer both sensible heat(temperature) and latent heat (moisture), ensuring unmatched efficiency in climate regulation.
This dual-transfer capability reduces heating/cooling loads, lowers energy consumption, and delivers consistent thermal comfort-a hallmark of Menred's innovation.
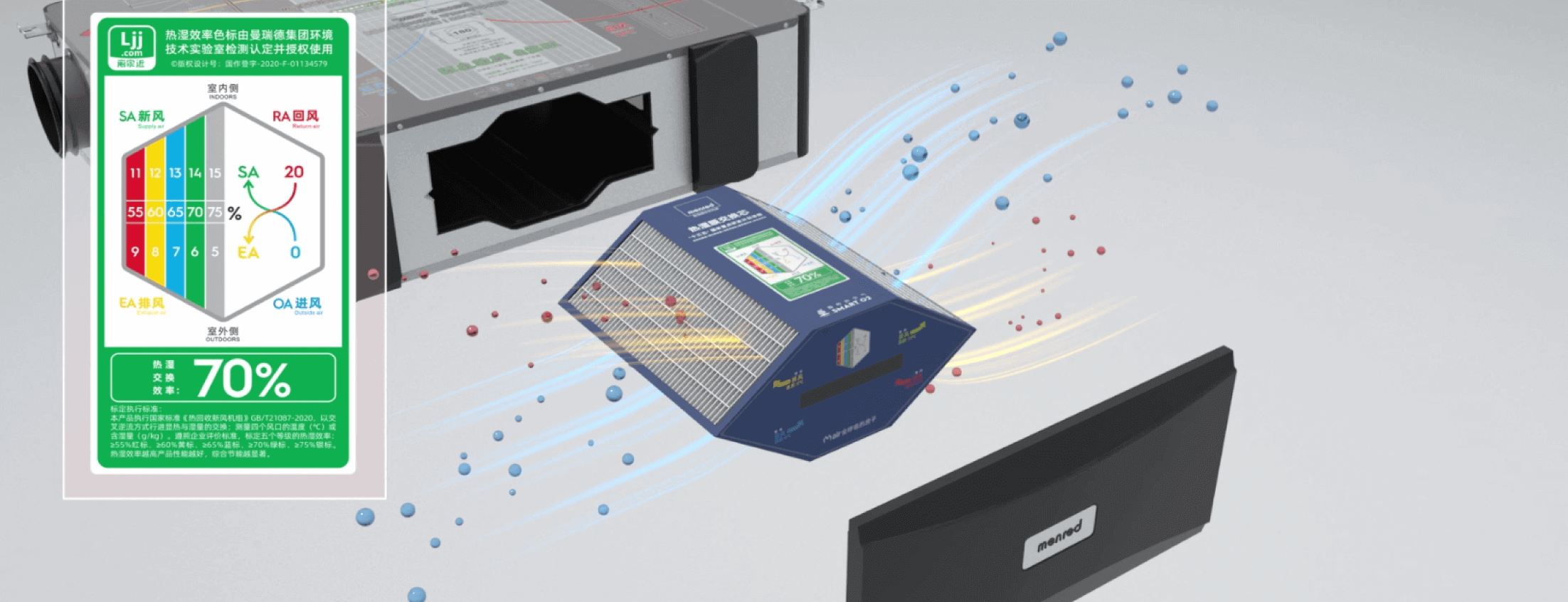
The working principle of an enthalpy heat exchanger revolves around the transfer of heat and moisture between two air streams—one carrying stale exhaust air and the other bringing in fresh outdoor air. The exchanger typically consists of a specialized core made from heat- and moisture-permeable materials that facilitate energy transfer without mixing the airstreams.
1.Airflow Exchange: Exhaust air from inside the building and fresh outdoor air pass through separate channels in the exchanger core.
2.Energy Transfer: The core material allows heat and moisture to transfer between the streams, reducing the temperature and humidity difference.
3.Conditioned Air Supply: The preconditioned fresh air is then distributed throughout the building, requiring less energy for heating or cooling.
This process ensures that the building maintains optimal indoor air quality while minimizing energy loss.
The terms enthalpy exchange and heat exchange are often used interchangeably, but they refer to different processes:
Heat Exchange: Focuses solely on transferring sensible heat (temperature) from one medium to another without considering moisture content. Examples include air-to-air plate heat exchangers and heat pipes.
Enthalpy Exchange: Involves transferring both sensible heat (temperature) and latent heat (moisture), which makes it particularly effective in humid climates.
While standard heat exchangers transfer only temperature, Menred's enthalpy systems go further by managing moisture-critical for humid climates.
By stabilizing humidity year-round, Menred prevents winter dryness and summer mold growth, outperforming conventional solutions.
Benefits of an Enthalpy Heat Exchanger
1. Significant Energy Savings
By recovering and reusing heat from exhaust air, enthalpy exchangers reduce the workload on HVAC systems, leading to lower energy consumption and operational costs.
2. Enhanced Indoor Air Quality
Fresh outdoor air is continuously supplied while stale indoor air is expelled, reducing pollutants, allergens, and excess humidity levels.
3. Improved Comfort and Humidity Control
Unlike standard heat exchangers, enthalpy exchangers regulate both temperature and moisture levels, ensuring a more comfortable indoor environment.
4. Reduced Carbon Footprint
Lower energy consumption directly translates to reduced greenhouse gas emissions, making enthalpy exchangers a sustainable choice.
5. Prevents Mold Growth and Condensation Issues
By maintaining balanced indoor humidity, these systems help prevent condensation and mold growth, which can lead to structural damage and health concerns.
Enthalpy heat exchangers are widely used in various settings, including:
Residential Homes: For improved ventilation and energy savings in houses and apartments.
Commercial Buildings: Offices, hotels, and shopping malls benefit from better air quality and reduced HVAC costs.
Industrial Facilities: Factories and warehouses require controlled humidity levels for operational efficiency.
Healthcare & Educational Institutions: Schools and hospitals rely on proper ventilation to maintain a safe and healthy environment.
When selecting an enthalpy heat exchanger, consider the following factors:
Core Material: Choose high-efficiency membranes that allow optimal heat and moisture transfer.
Climate Compatibility: Ensure the system suits your regional climate conditions for maximum energy savings.
System Capacity: Match the exchanger to your building’s ventilation needs.
Ease of Maintenance: Opt for models with accessible filters and durable core materials.
For superior performance, consider ventilators with Mair energy membrane exchange core.
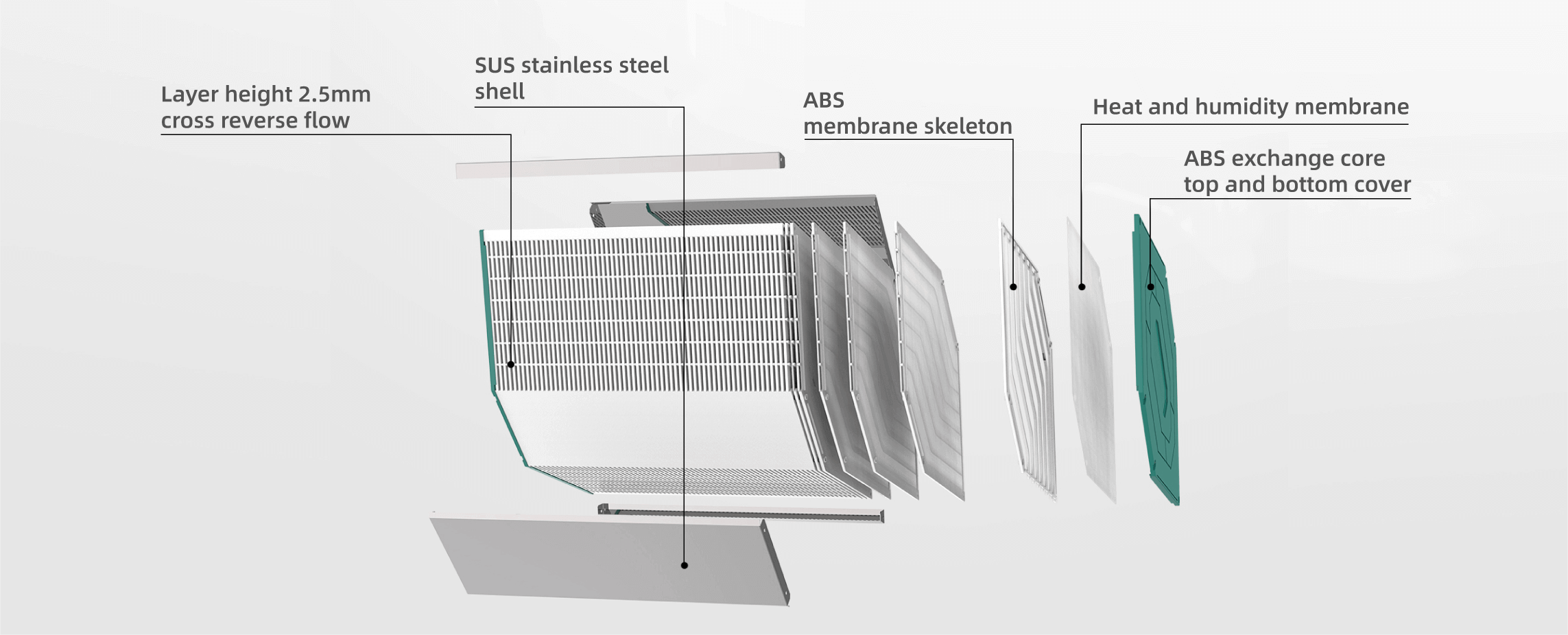
An enthalpy heat exchanger is a powerful solution for enhancing indoor air quality while reducing energy consumption. Its ability to transfer both heat and moisture makes it a must-have for any energy-efficient ventilation system. Whether for residential, commercial, or industrial use, these systems contribute to sustainability and long-term cost savings.
Menred's enthalpy heat exchangers redefine modern ventilation by merging energy savings with healthier air. As global demand for sustainability grows, investing in Menred's ERV technology delivers both environmental impact and long-term ROI.
