What is the purpose of an energy recovery ventilator?
views: 3726 time: 2024-10-12
views: 3726 time: 2024-10-12
An Energy Recovery Ventilator (ERV) is a mechanical device designed to improve indoor air quality by continuously exchanging stale indoor air with fresh outdoor air. The primary purpose of an ERV is to recover heat and moisture from the outgoing air and transfer it to the incoming air, thereby reducing energy consumption and maintaining a comfortable indoor environment. This is particularly useful in climates with extreme temperatures, where traditional ventilation systems might lead to significant energy loss.
An ERV can be highly beneficial, especially in scenarios where energy efficiency and indoor air quality are priorities. The savings on heating and cooling costs can offset the initial investment over time. Additionally, an ERV helps maintain humidity levels, which is crucial for comfort and health. In regions with high humidity or significant temperature fluctuations, an ERV can provide substantial value by reducing the load on HVAC systems and improving overall comfort.
Heat Recovery Ventilator (HRV): An HRV is designed to transfer only sensible heat (temperature) from the exhaust air to the incoming fresh air. It does not transfer moisture, making it more suitable for climates where humidity control is less of a concern. HRVs are effective in both heating and cooling seasons.
Energy Recovery Ventilator (ERV): An energy recovery ventilator(ERV) is a mechanical ventilation system that use a enthalpy exchanger to pre-cool or pre-heat incoming fresh air to reduce the demand on a building’s heating and cooling system, it play a very important role in the radiant heating and cooling system solution.
ERVs are different from heat recovery ventilators(HRV)because ERV goes a step further by not only transferring sensible heat but also latent heat (moisture). This makes ERVs ideal for climates where humidity control is a priority, such as in regions with high humidity or during seasons with significant humidity changes. ERVs are more complex and typically more expensive than HRVs.
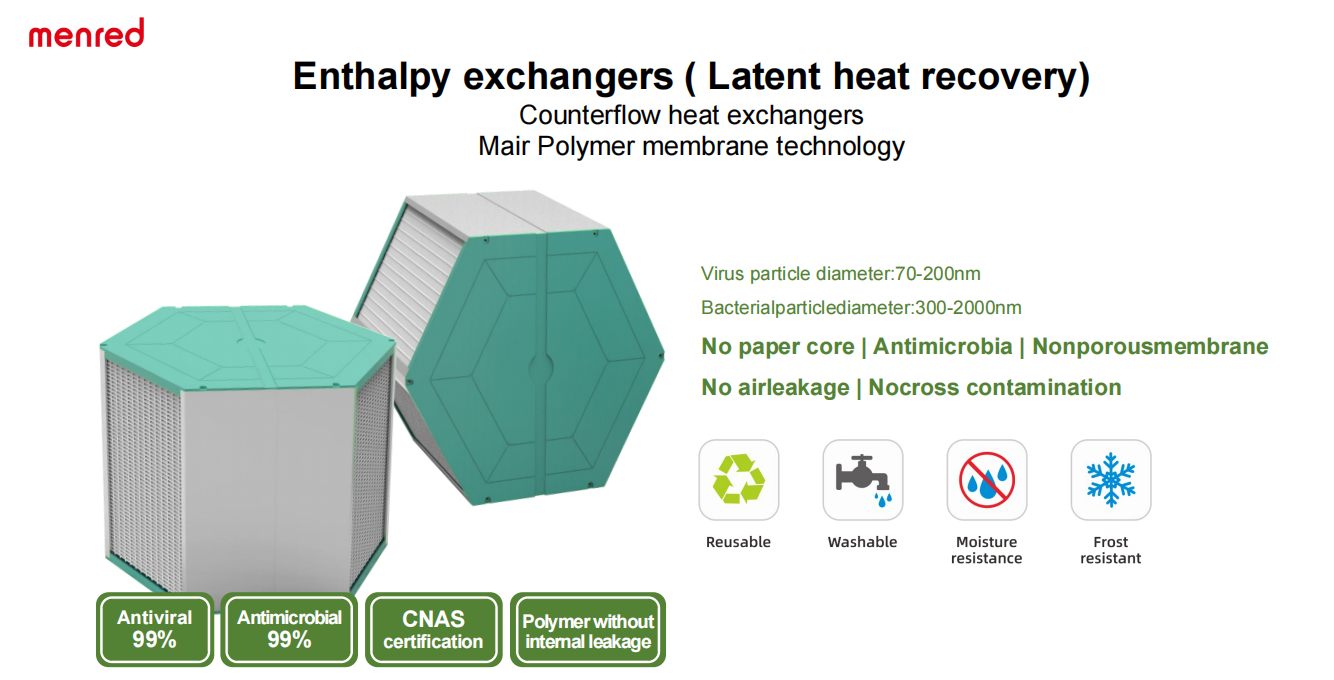
An energy recovery system is used to enhance the efficiency of HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) systems by recapturing energy from exhaust air and using it to condition incoming fresh air. This process helps in reducing the energy consumption associated with heating and cooling, thereby contributing to energy savings and lower operational costs. Additionally, energy recovery systems improve indoor air quality by ensuring a continuous supply of fresh air while maintaining optimal comfort levels.