What is an ERV
views: 11044 time: 2022-04-13
views: 11044 time: 2022-04-13
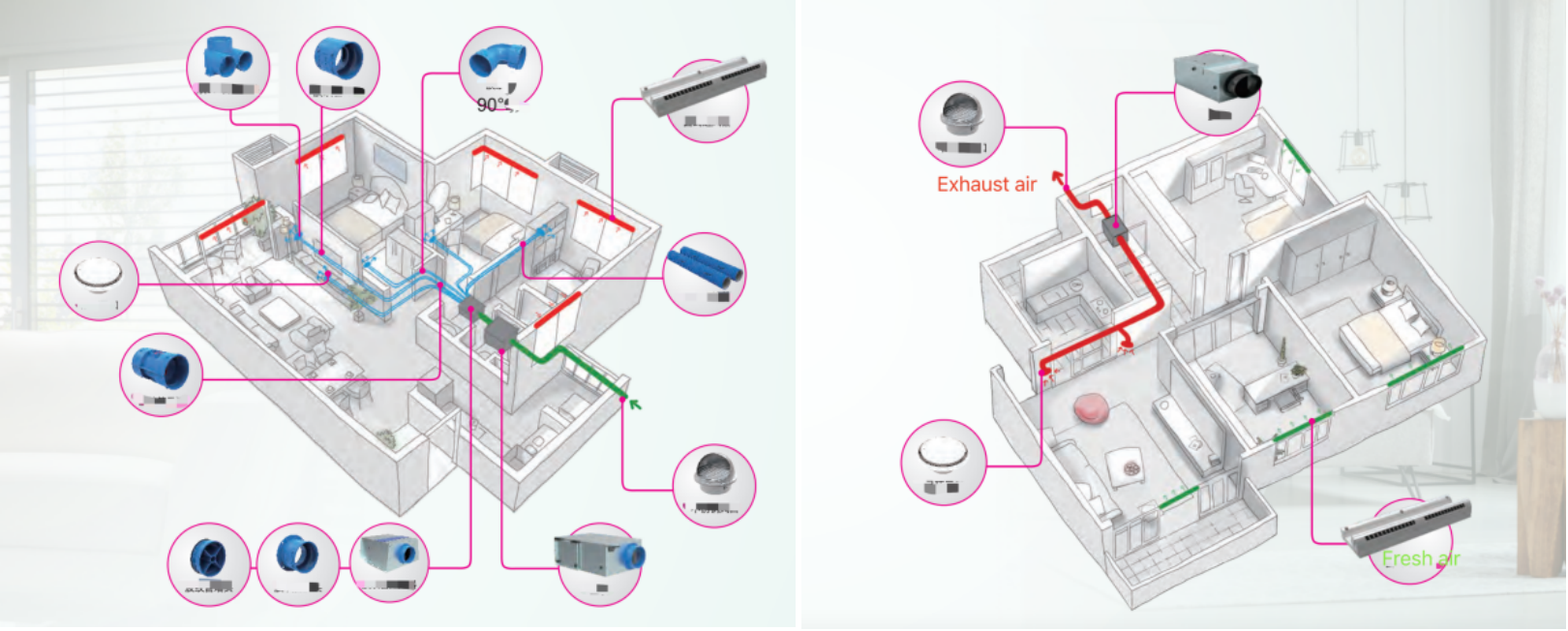
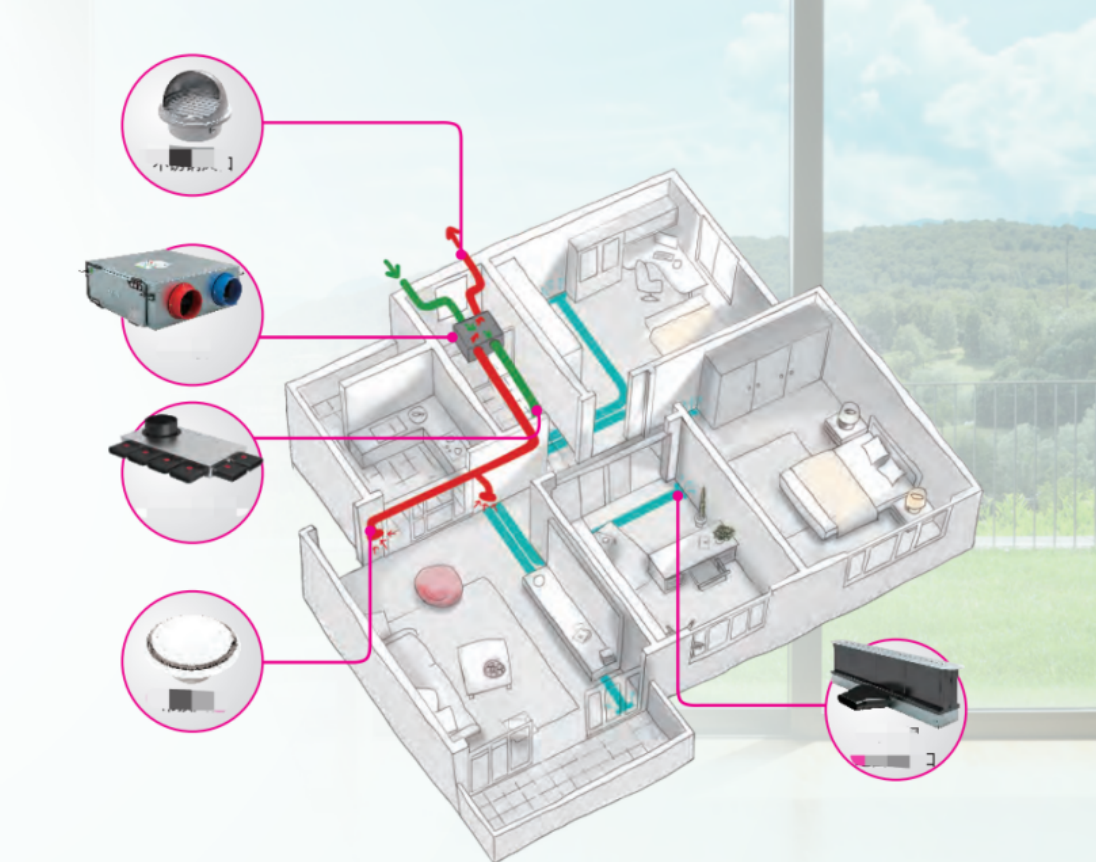
Theenergy recovery ventilation ERV system is based on the principle of supplying fresh air indoors with special equipment on one side of the room, and then discharging it to the outside from the other side by special equipment, forming a "fresh air flow field" indoors, so as to meet the needs of indoor fresh air ventilation. The German EBM DC vertical fresh airFan is used to supply air from the outside to the room by mechanical strength, and the other side is forced to form a fresh air flow field in the system by means of a specially designed exhaust fresh air blower to discharge it to the outside. While supplying air, the air entering the room is filtered, sterilized, oxygenated, and preheated (winter) by ERV system. When the exhaust air passes through the main engine, it exchanges heat with theoutside air, and most of the energy is recovered and sent back to the room through thesupply air. In order to achieve the purpose of indoor air purification environment.
First of all, pay attention to the use range of variousERV systems. For example, the use range ofoutdoor air processors is -5°C to 43°C. In areas where the calculated outdoor temperature in winter is below -5°C, it is not recommended to use paper-coreheat exchange., that will result the cores frozen, if it is to be used, an air preheater should be installed on the fresh air intake duct to preheat the fresh air, or a membrane core exchangeenergy recovery is completely recommend. The two air ducts (fresh air duct and exhaust air duct) connecting theERV exchanger to the outside should be set with a slope of not less than 0.03, and the slope should be directed to the outside to prevent condensed water or rainwater from entering the unit. It is necessary to pay attention to the noise problem. The noise marked on most of theERV exchanger samples is tested under the following conditions: installed in the ceiling of the room. Measured at 1.5 meters below the machine; when the actual engineering and test conditions are different, the noise will increase, and the greater the air volume, the greater the noise.
There are very strict standards in the installation design of theenergy recovery ventilation system. Friends who choose the fresh air system must invite professionals to install the system to ensure the use effect of theERV system
According to theair flow direction:It includes one-way ventilators and cross flow ventilators ( heat recovery ventilator HRVand energy recovery ventilator ERV)
One way ventilator
Positive pressure ventilator Negative pressure ventilator
(Cross flow ventilator)HRV and ERV
According to mounting type:Window intake fresh air ventilator, wall-mounted ventilator, ceiling type and vertical cabinet units.
The ventilator standard design for bedrooms is 30 cubic meters of fresh air per person per hour, and the standard for halls and commercial spaces is 0.6 changes per hour. Excessive air volume results in high noise, large energy loss, and frequent replacement of filter elements.
Reasonable distribution of indoor airflow (air pressure), different air pressures are designed for different rooms or areas. Make the fresh air diffuse more evenly, and more fully "drive off the exhaust gas" to the outside.
Positive pressure area: the bedroom should be positive pressure or slightly positive pressure (supply air)
Negative pressure area: toilet and kitchen are pollution source generating areas, which should be designed as negative pressure (return air).
Overflow area: the airflow channel between the positive pressure area and the negative pressure area, corridors, aisles, stairwells, etc..
Air intake: Outdoor fresh air intake, preferably a well-ventilated place on the south side of the house. It is forbidden to take air near the exhaust port of the stove, range hood and bathroom.
According to the outdoor air quality, the appropriate filter grade should be selected. The higher the efficiency, the greater the wind resistance; the greater the power consumption and wind noise of the fan (per cubic air ≤ 0.45W/h); the pursuit of PM2.5 as "zero" is somewhat extreme which isunreasonable.
The treatment of formaldehyde andVOC technology directly quoted from the air purifier. Fresh air purification(ventilation system) is completely different, thatexhaust gas is discharged outside and take infresh air, there is no formaldehyde and VOC in the outdoor air, these functions are not used! The most effective and easiest way to reduce indoor formaldehyde is ventilation.
PM2.5 haze removal grade: excellent 35ug/m3, good 35~75ug/m3, light pollution 75~115ug/m3 moderate pollution 115~150ug/m3; heavy pollution 150~250ug/m3; serious pollution 250ug/m3 and above /m3 . Note: 24-hour PM2.5 average.
Heat and moisture recovery: reduce heat loss during ventilation (recommended ≥75%), dehumidify in summer/moisturize in winter.
Ventilation: ensure that the carbon dioxide concentration does not exceed the standard (≤700ppm)